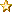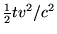From this there ensues the following peculiar consequence. If at the points A and B of K there are stationary clocks which, viewed in the stationary system, are synchronous; and if the clock at A is moved with the velocity v along the line AB to B, then on its arrival at B the two clocks no longer synchronize, but the clock moved from A to B lags behind the other which has remained at B by
(up to magnitudes of fourth and higher order), t being the time occupied in the journey from A to B.
It is at once apparent that this result still holds good if the clock moves from A to B in any polygonal line, and also when the points A and B coincide.
If we assume that the result proved for a polygonal line is also valid for a continuously curved line, we arrive at this result: If one of two synchronous clocks at A is moved in a closed curve with constant velocity until it returns to A, the journey lasting t seconds, then by the clock which has remained at rest the travelled clock on its arrival at A will be
second slow. Thence we conclude that a balance-clock at the equator must go more slowly, by a very small amount, than a precisely similar clock situated at one of the poles under otherwise identical conditions.